Share this
Why Edge Computing Is Important for Industry 4.0 Success
by Brett Daniel on Dec 11, 2020 1:44:17 PM

Photo: Edge computing is and will continue to be an integral part of industry 4.0, otherwise known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Learn more about it and its place in the fast-advancing world of manufacturing in this blog post.
We’ve talked about tactical edge servers and how they’re improving the effectiveness of UAV operations, but on a scale much larger than the military alone, edge computing is poised to bring forth massive change in the global economy by altering, upgrading, and replacing the manufacturing and production technologies implemented during the previous industrial revolution.
There’s a trendy name for this phenomenon – industry 4.0 – coined by the German government in 2011 to describe its initiatives in manufacturing digitalization. It aims to “drive digital manufacturing forward by increasing digitization and the interconnection of products, value chains, and business models. It also aims to support research, the networking of industry partners, and standardization.”
But industry 4.0 is not just a trend; it’s an entire revolution in manufacturing and production that’s here to stay.
According to B2B research company MarketsandMarkets, the global industrial internet of things (IIoT) platform market size is expected to reach $13.82 billion by 2023.
Now do I have your attention?
In this blog post, we’ll discuss industry 4.0, or the Fourth Industrial Revolution, edge computing, and how the two are related, or in our opinion, inseparable. Toward the end, we’ll provide use cases to demonstrate the relationship between the two and discuss some things to keep in mind as you explore rugged computing solutions for your edge-driven industry 4.0 deployments.

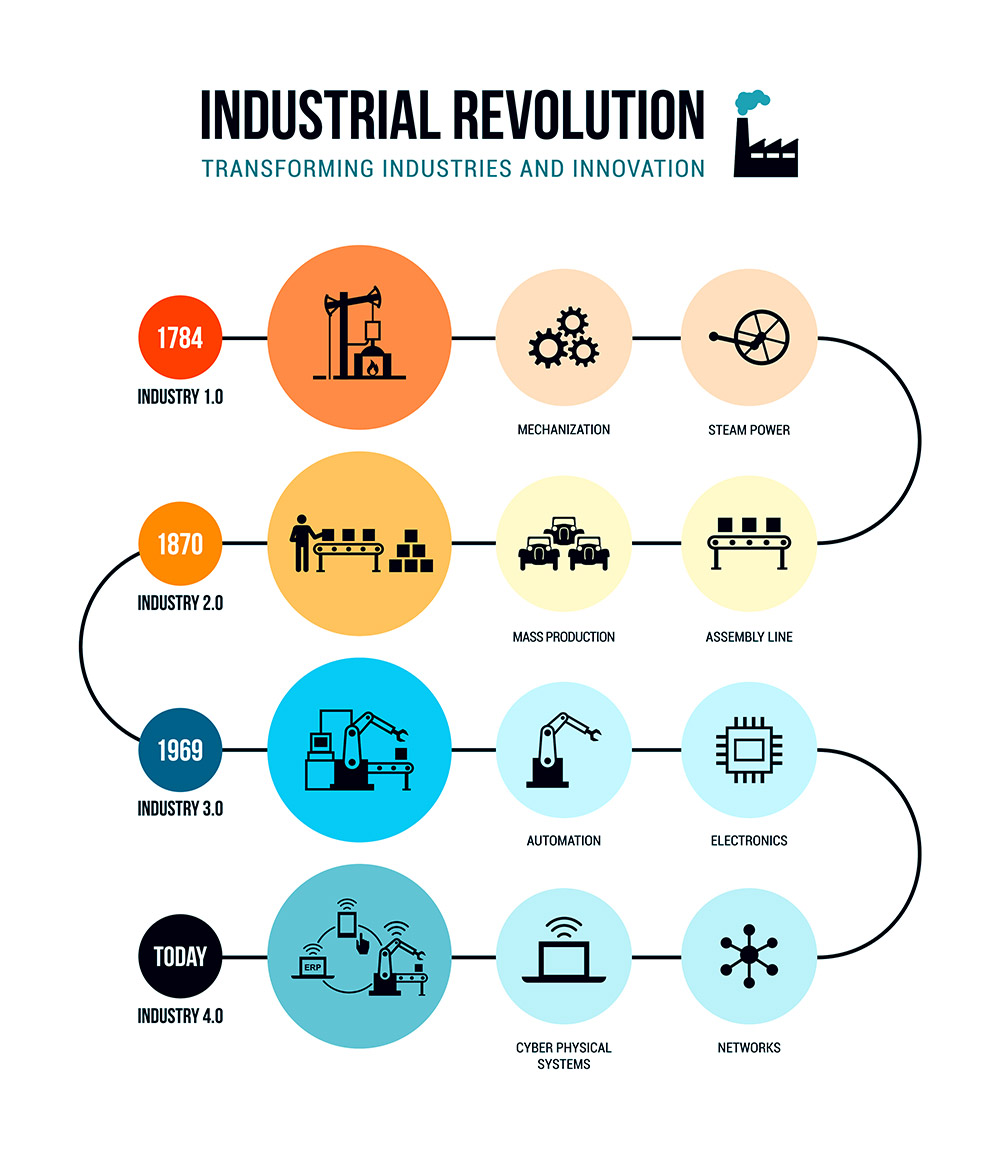
Graphic: Industry 4.0 has its roots in the computerization of manufacturing and production processes. It is sometimes referred to as "smart manufacturing," and you have heard of the term "smart factory," in which technological processes are highly integrated to achieve productivity goals faster and more efficiently.
What is industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is both a concept and a revolution.
Conceptually, industry 4.0 broadly refers to a variety of ongoing technological advancements and practices being implemented by businesses and organizations globally to improve the speed and efficiency of their manufacturing and production processes.
These advancements and practices include the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), big data analysis, 5G cellular technology, 3D printing, edge computing and smart sensors, among other advanced technologies, to boost production rate, cut manufacturing costs, streamline communication and responsiveness between automated machines, achieve manufacturing and productivity objectives faster by increasing the speed, efficiency, precision, and accuracy of assembly line processes and related data, and more.
Graphic: Cyber-physical systems, or systems that integrate the power of computation with physical objects and processes, such as those seen in sensor networks and automated machines, are expected to dominate the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Industry 4.0 may also refer to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which is the phase of industrial advancement in which humanity currently finds itself. The Fourth Industrial Revolution is a direct result of the advancements and practices mentioned earlier, with a strong emphasis on less human intervention in manufacturing and production, not for the purpose of eliminating human involvement entirely, but rather to develop a highly adept, technologically assisted workforce.
A total of nine pillars, or technological drivers, have been broadly defined as contributors to industry 4.0, or the Fourth Industrial Revolution. They are:
- Big data, to better inform and empower companies’ organizational decision-making
- Autonomous robots, to quickly and efficiently solve complex tasks that humans cannot solve with ease
- Simulation and mathematical modeling, to optimize the manufacturing and production processes and achieve effective shop-floor management
- Horizontal and vertical system integration, to ensure connectivity amongst in-house machines and between supply chain partners
- Industrial internet of things (IIoT), to gather, process, and store data from physical objects within manufacturing and production environments, and to use it to improve operations
- The cloud, to assist with supply chain integration, facilitate its management and administration, and virtualize resources to streamline traditional client-server infrastructure
- Additive manufacturing, to reduce lead times and allow for quicker and better design and prototype production
- Augmented reality (AR), to enhance human-machine interaction, maintenance tasks, and equipment inspections
- Cybersecurity, to safeguard the data circulating in manufacturing and production environments

Graphic: Edge computing has its place in the middle, or at the edge, of cloud computing and the internet of things (IoT). It is essential to ensure the success of industry 4.0 going forward.
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is a distributed networking architecture focused on moving the computational power of the cloud nearer to data-generating sources to reduce latency and cut data transfer costs.
Edge computing achieves its low latency by reducing the physical distance that data must travel for processing and analysis. In a conventional cloud computing architecture, servers in a remote, centralized cloud data center process incoming data and return insights gleaned from this data to the end user. But because of their remoteness, the data traveling to them travels farther than in an edge computing architecture, an additional distance that results in greater network latency, or a delay in data transfer, which is a major problem for applications requiring real-time responses and data-driven insights.

Graphic: Edge computing complements the smart manufacturing processes of the future, ensuring that employees and management teams have quick access to the insights they need to bolster productivity.
Why is edge computing important for industry 4.0 success?
Edge computing and industry 4.0 cross paths in what's known as "industrial edge computing." Industrial edge computing describes the incorporation of edge computing technologies, such as edge servers, into modernized, data-driven manufacturing and production environments, like those indicative of industry 4.0.
The relationship between edge computing and industry 4.0 is already being realized in the form of on-site data centers, which go by a few different names, but essentially refer to the same technology. You may have heard of them referred to as “micro data centers,” “edge data centers,” or “containerized data centers.”
These local data centers are placed near data-generating sources – think of all the different data-collecting machines and IIoT devices in a smart factory, or for our defense and aerospace readers, the different vehicle, aircraft, and soldier sensors collecting data in the field – to improve response times, and in turn, boost speed, efficiency, and supervisory decision-making.
Now, think of the benefits this brings. Your automated manufacturing and production processes benefit from quicker insights, your big data infrastructure is more reliable, and your management team has the data it needs, faster, to make decisions, faster, which increases productivity at all levels of management, including logistics, operations, maintenance, quality, and general management, not to mention on the floor itself.
Edge computing is arguably the 10th pillar of industry 4.0, or it could be considered a supplement to the cloud computing pillar, given that the two function in tandem with each other. In the next section, we’ll provide some use cases to aid in your understanding of how edge computing and industry 4.0 are a match made in smart manufacturing heaven.

Graphic: Edge computing has its place in numerous industry 4.0 use cases.
Two scenarios for edge computing and industry 4.0
We have written two separate scenarios to showcase the positive relationship between edge computing and industry 4.0.
- Equipment uptime and predictive maintenance scenario: IIoT sensors attached to an assembly line robot regularly transfer speed, temperature, and volume data to a nearby edge server, which, thanks to its proximity, can quickly analyze it and deliver machine health and productivity insights to a maintenance and operations supervisor. One day, the supervisor notices frequent temperature spikes indicative of a potential overheating event. So, to prevent assembly line downtime, as well as costly damage to the robot and other equipment on the floor, the supervisor takes preemptive steps to solve the problem, an otherwise impossible feat without edge computing and industry 4.0 technologies.
- Computer vision system and quality scenario: A computer vision system in a factory uses specialized cameras to monitor the quality of products traveling on a fast-moving conveyor belt. An edge server deployed nearby generates reports based on the data the system collects and can also use it to instruct the system to tell a robotic arm installed near the belt to remove any defective or otherwise low-quality products. One day, the robotic arm quickly removes a defective product as soon as the system notices it. Perfectly high-quality products on the conveyor belt were not removed, nor was the conveyor belt disrupted, because of a delayed response. Consider the outcome without the real-time response due to the deployment of an edge server.

Photo: Securing everything you need in an edge server for your IIoT application is stressful enough. We've made it easier for you by covering the business bases below.
Conclusion: 10 Questions to Ask Edge Server Manufacturers
As businesses and organizations continue to digitize their manufacturing and production processes, the adoption of edge servers and edge data centers will continue to increase.
Partnering with server manufacturers that not only keep pace with changing technological trends, like edge computing and industry 4.0, but that also have a reputation for outstanding quality and performance is crucial.
Here are 10 questions you can ask to generate discussion and help you determine whether an edge server manufacturer is the right fit:
- Have you successfully deployed edge servers for the industry 4.0 pillars discussed in this blog post - big data, automation, additive manufacturing, or the others - and can you provide examples of their continued success?
- What are your internal cybersecurity practices, and do you offer any custom options or additional hardware and software, such as custom BIOSes, TCG Opal 2.0 or Enterprise self-encrypting drives, and advanced Linux operating system security software, that will further protect my edge server?
- What sorts of quality, compliance, and counterfeit protection programs do you have in place to ensure the reliability and security of my edge server once it leaves your facility?
- Where do you source your hardware, and do you have partnerships with leading computer hardware manufacturers, such as Intel and NVIDIA, to ensure that my solution always has the latest and greatest technology?
- Would you be willing to let me test the solution for an extended period without charge?
- Where do you perform your compliance testing?
- Will you describe the terms and conditions of your warranty?
- How do you handle revision and obsolescence control?
- Where is your support team located should I need answers to my questions fast?
- To what extent is your engineering team able to offer me a custom computing solution, particularly with regard to high-performance data storage and processing at the edge?
As always, Trenton Systems is here to answer these questions and more should you be interested in choosing the world's leading made-in-USA rugged computing solutions manufacturer for your edge server deployment.
We're here when you're ready.
Share this
- High-performance computers (42)
- Military computers (38)
- Rugged computers (32)
- Cybersecurity (25)
- Industrial computers (25)
- Military servers (24)
- MIL-SPEC (20)
- Rugged servers (19)
- Press Release (17)
- Industrial servers (16)
- MIL-STD-810 (16)
- 5G Technology (14)
- Intel (13)
- Rack mount servers (12)
- processing (12)
- Computer hardware (11)
- Edge computing (11)
- Rugged workstations (11)
- Made in USA (10)
- Partnerships (9)
- Rugged computing (9)
- Sales, Marketing, and Business Development (9)
- Trenton Systems (9)
- networking (9)
- Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) (7)
- Encryption (6)
- Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) (6)
- GPUs (6)
- IPU (6)
- Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) (6)
- Server motherboards (6)
- artificial intelligence (6)
- Computer stress tests (5)
- Cross domain solutions (5)
- Mission-critical servers (5)
- Rugged mini PCs (5)
- AI (4)
- BIOS (4)
- CPU (4)
- Defense (4)
- Military primes (4)
- Mission-critical systems (4)
- Platform Firmware Resilience (PFR) (4)
- Rugged blade servers (4)
- containerization (4)
- data protection (4)
- virtualization (4)
- Counterfeit electronic parts (3)
- DO-160 (3)
- Edge servers (3)
- Firmware (3)
- HPC (3)
- Just a Bunch of Disks (JBOD) (3)
- Leadership (3)
- Navy (3)
- O-RAN (3)
- RAID (3)
- RAM (3)
- Revision control (3)
- Ruggedization (3)
- SATCOM (3)
- Storage servers (3)
- Supply chain (3)
- Tactical Advanced Computer (TAC) (3)
- Wide-temp computers (3)
- computers made in the USA (3)
- data transfer (3)
- deep learning (3)
- embedded computers (3)
- embedded systems (3)
- firmware security (3)
- machine learning (3)
- Automatic test equipment (ATE) (2)
- C6ISR (2)
- COTS (2)
- COVID-19 (2)
- CPUs (2)
- Compliance (2)
- Compute Express Link (CXL) (2)
- Computer networking (2)
- Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) (2)
- DDR (2)
- DDR4 (2)
- DPU (2)
- Dual CPU motherboards (2)
- EW (2)
- I/O (2)
- Military standards (2)
- NVIDIA (2)
- NVMe SSDs (2)
- PCIe (2)
- PCIe 4.0 (2)
- PCIe 5.0 (2)
- RAN (2)
- SIGINT (2)
- SWaP-C (2)
- Software Guard Extensions (SGX) (2)
- Submarines (2)
- Supply chain security (2)
- TAA compliance (2)
- airborne (2)
- as9100d (2)
- chassis (2)
- data diode (2)
- end-to-end solution (2)
- hardware security (2)
- hardware virtualization (2)
- integrated combat system (2)
- manufacturing reps (2)
- memory (2)
- mission computers (2)
- private 5G (2)
- protection (2)
- secure by design (2)
- small form factor (2)
- software security (2)
- vRAN (2)
- zero trust (2)
- zero trust architecture (2)
- 3U BAM Server (1)
- 4G (1)
- 4U (1)
- 5G Frequencies (1)
- 5G Frequency Bands (1)
- AI/ML/DL (1)
- Access CDS (1)
- Aegis Combat System (1)
- Armed Forces (1)
- Asymmetric encryption (1)
- C-RAN (1)
- COMINT (1)
- Cloud-based CDS (1)
- Coast Guard (1)
- Compliance testing (1)
- Computer life cycle (1)
- Containers (1)
- D-RAN (1)
- DART (1)
- DDR5 (1)
- DMEA (1)
- Data Center Modular Hardware System (DC-MHS) (1)
- Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) (1)
- Defense Advanced Research Projects (DARP) (1)
- ELINT (1)
- EMI (1)
- EO/IR (1)
- Electromagnetic Interference (1)
- Electronic Warfare (EW) (1)
- FIPS 140-2 (1)
- FIPS 140-3 (1)
- Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) (1)
- Ground Control Stations (GCS) (1)
- Hardware-based CDS (1)
- Hybrid CDS (1)
- IES.5G (1)
- ION Mini PC (1)
- IP Ratings (1)
- IPMI (1)
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) (1)
- Industry news (1)
- Integrated Base Defense (IBD) (1)
- LAN ports (1)
- LTE (1)
- Life cycle management (1)
- Lockheed Martin (1)
- MIL-S-901 (1)
- MIL-STD-167-1 (1)
- MIL-STD-461 (1)
- MIL-STD-464 (1)
- MOSA (1)
- Multi-Access Edge Computing (1)
- NASA (1)
- NIC (1)
- NIC Card (1)
- NVMe (1)
- O-RAN compliant (1)
- Oil and Gas (1)
- Open Compute Project (OCP) (1)
- OpenRAN (1)
- P4 (1)
- PCIe card (1)
- PCIe lane (1)
- PCIe slot (1)
- Precision timestamping (1)
- Product life cycle (1)
- ROM (1)
- Raytheon (1)
- Remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) (1)
- Rugged computing glossary (1)
- SEDs (1)
- SIM Card (1)
- Secure boot (1)
- Sensor Open Systems Architecture (SOSA) (1)
- Small form-factor pluggable (SFP) (1)
- Smart Edge (1)
- Smart NIC (1)
- SmartNIC (1)
- Software-based CDS (1)
- Symmetric encryption (1)
- System hardening (1)
- System hardening best practices (1)
- TME (1)
- Tech Partners (1)
- Total Memory Encryption (TME) (1)
- Transfer CDS (1)
- USB ports (1)
- VMEbus International Trade Association (VITA) (1)
- Vertical Lift Consortium (VLC) (1)
- Virtual machines (1)
- What are embedded systems? (1)
- Wired access backhaul (1)
- Wireless access backhaul (1)
- accredidation (1)
- aerospace (1)
- air gaps (1)
- airborne computers (1)
- asteroid (1)
- authentication (1)
- autonomous (1)
- certification (1)
- cognitive software-defined radios (CDRS) (1)
- command and control (C2) (1)
- communications (1)
- cores (1)
- custom (1)
- customer service (1)
- customer support (1)
- data linking (1)
- data recording (1)
- ethernet (1)
- full disk encryption (1)
- hardware monitoring (1)
- heat sink (1)
- hypervisor (1)
- in-house technical support (1)
- input (1)
- integrated edge solution (1)
- international business (1)
- licensed spectrum (1)
- liquid cooling (1)
- mCOTS (1)
- microelectronics (1)
- missile defense (1)
- mixed criticality (1)
- moving (1)
- multi-factor authentication (1)
- network slicing (1)
- neural networks (1)
- new headquarters (1)
- next generation interceptor (1)
- non-volatile memory (1)
- operating system (1)
- output (1)
- outsourced technical support (1)
- post-boot (1)
- pre-boot (1)
- private networks (1)
- public networks (1)
- radio access network (RAN) (1)
- reconnaissance (1)
- rugged memory (1)
- secure flash (1)
- security (1)
- self-encrypting drives (SEDs) (1)
- sff (1)
- software (1)
- software-defined radios (SDRs) (1)
- speeds and feeds (1)
- standalone (1)
- storage (1)
- systems (1)
- tactical wide area networks (1)
- technical support (1)
- technology (1)
- third-party motherboards (1)
- troposcatter communication (1)
- unlicensed spectrum (1)
- volatile memory (1)
- vpx (1)
- zero trust network (1)
- January 2025 (1)
- November 2024 (1)
- October 2024 (1)
- August 2024 (1)
- July 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (1)
- April 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (1)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (7)
- April 2023 (5)
- March 2023 (7)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (6)
- October 2022 (7)
- September 2022 (8)
- August 2022 (3)
- July 2022 (4)
- June 2022 (13)
- May 2022 (10)
- April 2022 (4)
- March 2022 (11)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (4)
- December 2021 (1)
- November 2021 (4)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (1)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (3)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (3)
- March 2021 (3)
- February 2021 (8)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (5)
- November 2020 (5)
- October 2020 (4)
- September 2020 (4)
- August 2020 (6)
- July 2020 (9)
- June 2020 (11)
- May 2020 (13)
- April 2020 (8)
- February 2020 (1)
- January 2020 (1)
- October 2019 (1)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (2)
- March 2019 (1)
- January 2019 (2)
- December 2018 (1)
- November 2018 (2)
- October 2018 (5)
- September 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (1)
- April 2018 (2)
- March 2018 (1)
- February 2018 (9)
- January 2018 (27)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (3)
/Trenton%20Systems%20Circular%20Logo-3.png?width=50&height=50&name=Trenton%20Systems%20Circular%20Logo-3.png)

No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think