Share this
Your All-in-One Guide to Trenton's Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processor Configurations
by Christopher Trick on Apr 15, 2024 10:51:14 AM

Depending upon your workload requirements, budget, and/or use case, there are many different CPUs that can be used to meet the technical and performance demands of a specific application or program.
In this blog, we'll dive into some of the main factors to look at when evaluating CPUs, the advantages of using Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors, and Trenton configurations utilizing these processors to cater to diverse customer requirements.
What are some of the main factors to look at when evaluating a CPU?
When evaluating a CPU, it is critical to evaluate which factors directly impact performance, power consumption, and thermal characteristics.
Four of the most important factors are: cores, frequency, TDP, and threads. Let's take a look at each.
Cores
Cores refer to individual processing units within a CPU. They execute instructions and perform calculations.
Cores enable parallel processing, allowing multiple tasks to be executed simultaneously. More cores generally lead to improved multitasking and performance for tasks that can be parallelized.
Frequency
Frequency refers to the clock speed of a CPU. It represents how many instructions the CPU can execute per second when dealing with a single task.
Higher frequency CPUs can perform more computations in less time, leading to faster processing speeds. Increased frequency often correlates with improved overall performance in tasks that are not heavily parallelized.
TDP (Thermal Design Power)
TDP represents the maximum amount of heat generated by a CPU that the cooling system in a computer is designed to dissipate under typical workloads.
TDP provides a guideline for selecting appropriate cooling solutions to maintain stable operation of the CPU. Lower TDP CPUs generally consume less power and produce less heat, leading to greater energy efficiency and potentially quieter operation.
Threads
Threads represent the smallest unit of execution within a process. They allow a CPU to perform multiple tasks concurrently within a single process.
Threads enable better utilization of CPU resources by allowing simultaneous execution of multiple tasks. They facilitate efficient multitasking and responsiveness in applications.
Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors: A True Performance Boost
Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors are a family of high-performance server and workstation processors designed for enterprise deployments and mission-critical applications.
Introduced in 2017, these processors are highly scalable, offering configurations ranging from a few cores to dozens of cores, with support for multiple sockets in a single system. With built-in accelerators and chip-level technologies, these CPUs are optimized for the most demanding high-performance computing workloads.
There are four tiers of Xeon® Scalable Processors: Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum (in ascending order). These tiers indicate various levels of capabilities and are associated with factors such as core count, clock speed, power efficiency, and additional features such as advanced security measures or support for specific technologies.
Trenton Configurations with Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors
For over 30 years, Trenton Systems and Intel® have partnered to deliver high-performance computing solutions with cutting-edge processors for applications across the defense, government, industrial, and commercial markets.
We utilize single or dual 2nd to 5th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors within configurable and custom solutions to provide enhanced processing power, and these CPUs have built-in accelerators for AI/ML/DL, networking, security, and storage.
Take a look at the table below to see the performance ranges provided by the Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors running on Trenton solutions:
| Processor Generation | Cores | Frequency | TDP | Threads |
| 2nd Gen Xeon® SP | 4C-22C | 1.9GHz-4.0GHz | 70W-130W | 8T-44T |
| 3rd Gen Xeon® SP | 8C-32C | 2.0GHz-3.7GHz | 105W-235W | 16T-64T |
| 4th Gen Xeon® SP | 8C-32C | 1.8GHz-4.2GHz | 150W-250W | 16T-64T |
| 5th Gen Xeon® SP | 8C-36C | 2.2GHz-4.1GHz | 165W-270W | 16T-72T |
*4th and 5th Gen CPUs serve as drop-in replacements, allowing you to make upgrades with ease.
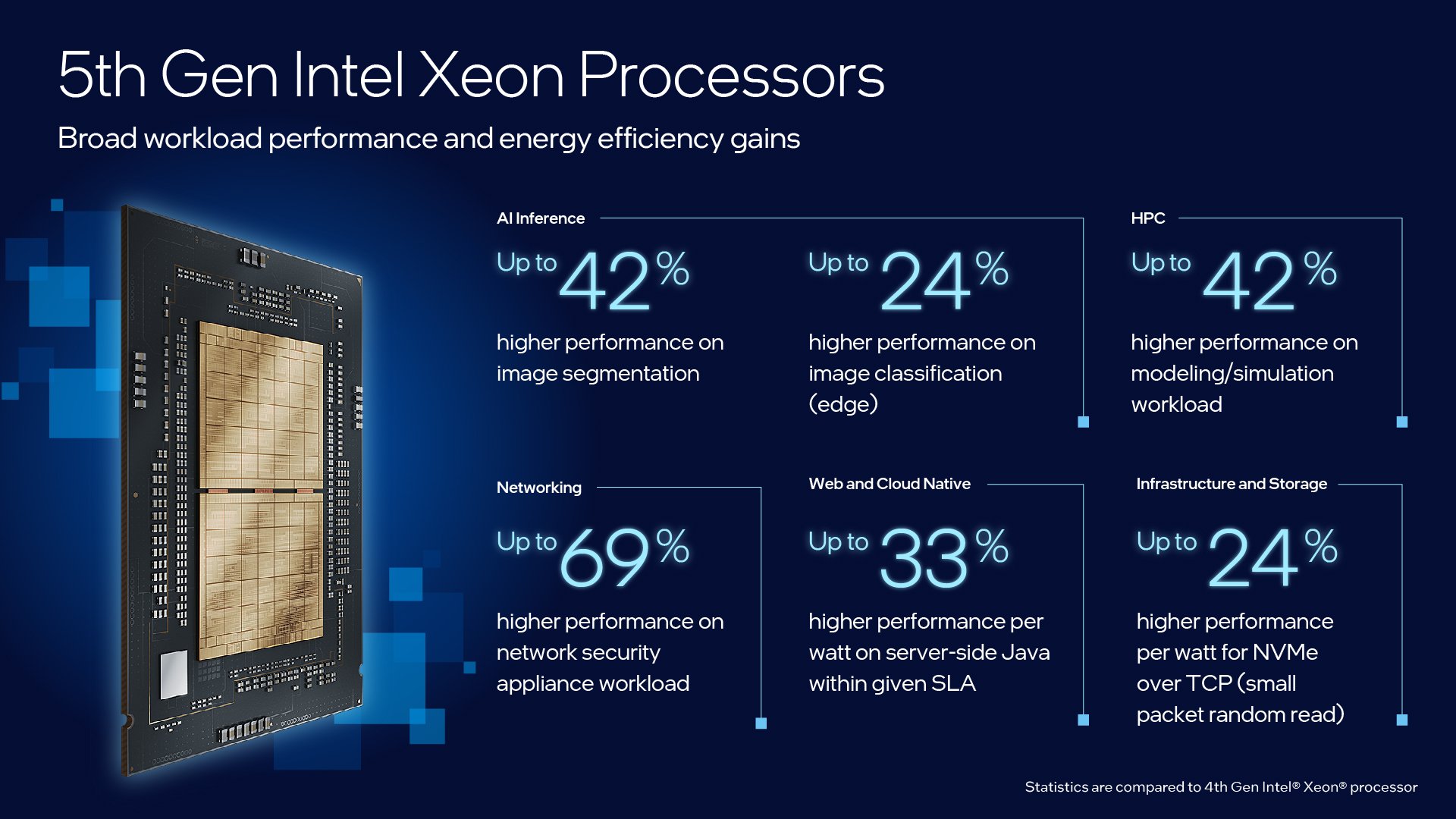
Generally, each CPU generation offers significant performance improvements over the previous generation. Here, for example, is a graphic that depicts the performance improvements of 5th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors:
For a comprehensive list of Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processor specs, click here.
Final Thoughts
Share this
- High-performance computers (42)
- Military computers (38)
- Rugged computers (32)
- Cybersecurity (25)
- Industrial computers (25)
- Military servers (24)
- MIL-SPEC (20)
- Rugged servers (19)
- Press Release (17)
- Industrial servers (16)
- MIL-STD-810 (16)
- 5G Technology (14)
- Intel (13)
- Rack mount servers (12)
- processing (12)
- Computer hardware (11)
- Edge computing (11)
- Rugged workstations (11)
- Made in USA (10)
- Partnerships (9)
- Rugged computing (9)
- Sales, Marketing, and Business Development (9)
- Trenton Systems (9)
- networking (9)
- Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) (7)
- Encryption (6)
- Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) (6)
- GPUs (6)
- IPU (6)
- Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) (6)
- Server motherboards (6)
- artificial intelligence (6)
- Computer stress tests (5)
- Cross domain solutions (5)
- Mission-critical servers (5)
- Rugged mini PCs (5)
- AI (4)
- BIOS (4)
- CPU (4)
- Defense (4)
- Military primes (4)
- Mission-critical systems (4)
- Platform Firmware Resilience (PFR) (4)
- Rugged blade servers (4)
- containerization (4)
- data protection (4)
- virtualization (4)
- Counterfeit electronic parts (3)
- DO-160 (3)
- Edge servers (3)
- Firmware (3)
- HPC (3)
- Just a Bunch of Disks (JBOD) (3)
- Leadership (3)
- Navy (3)
- O-RAN (3)
- RAID (3)
- RAM (3)
- Revision control (3)
- Ruggedization (3)
- SATCOM (3)
- Storage servers (3)
- Supply chain (3)
- Tactical Advanced Computer (TAC) (3)
- Wide-temp computers (3)
- computers made in the USA (3)
- data transfer (3)
- deep learning (3)
- embedded computers (3)
- embedded systems (3)
- firmware security (3)
- machine learning (3)
- Automatic test equipment (ATE) (2)
- C6ISR (2)
- COTS (2)
- COVID-19 (2)
- CPUs (2)
- Compliance (2)
- Compute Express Link (CXL) (2)
- Computer networking (2)
- Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) (2)
- DDR (2)
- DDR4 (2)
- DPU (2)
- Dual CPU motherboards (2)
- EW (2)
- I/O (2)
- Military standards (2)
- NVIDIA (2)
- NVMe SSDs (2)
- PCIe (2)
- PCIe 4.0 (2)
- PCIe 5.0 (2)
- RAN (2)
- SIGINT (2)
- SWaP-C (2)
- Software Guard Extensions (SGX) (2)
- Submarines (2)
- Supply chain security (2)
- TAA compliance (2)
- airborne (2)
- as9100d (2)
- chassis (2)
- data diode (2)
- end-to-end solution (2)
- hardware security (2)
- hardware virtualization (2)
- integrated combat system (2)
- manufacturing reps (2)
- memory (2)
- mission computers (2)
- private 5G (2)
- protection (2)
- secure by design (2)
- small form factor (2)
- software security (2)
- vRAN (2)
- zero trust (2)
- zero trust architecture (2)
- 3U BAM Server (1)
- 4G (1)
- 4U (1)
- 5G Frequencies (1)
- 5G Frequency Bands (1)
- AI/ML/DL (1)
- Access CDS (1)
- Aegis Combat System (1)
- Armed Forces (1)
- Asymmetric encryption (1)
- C-RAN (1)
- COMINT (1)
- Cloud-based CDS (1)
- Coast Guard (1)
- Compliance testing (1)
- Computer life cycle (1)
- Containers (1)
- D-RAN (1)
- DART (1)
- DDR5 (1)
- DMEA (1)
- Data Center Modular Hardware System (DC-MHS) (1)
- Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) (1)
- Defense Advanced Research Projects (DARP) (1)
- ELINT (1)
- EMI (1)
- EO/IR (1)
- Electromagnetic Interference (1)
- Electronic Warfare (EW) (1)
- FIPS 140-2 (1)
- FIPS 140-3 (1)
- Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) (1)
- Ground Control Stations (GCS) (1)
- Hardware-based CDS (1)
- Hybrid CDS (1)
- IES.5G (1)
- ION Mini PC (1)
- IP Ratings (1)
- IPMI (1)
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) (1)
- Industry news (1)
- Integrated Base Defense (IBD) (1)
- LAN ports (1)
- LTE (1)
- Life cycle management (1)
- Lockheed Martin (1)
- MIL-S-901 (1)
- MIL-STD-167-1 (1)
- MIL-STD-461 (1)
- MIL-STD-464 (1)
- MOSA (1)
- Multi-Access Edge Computing (1)
- NASA (1)
- NIC (1)
- NIC Card (1)
- NVMe (1)
- O-RAN compliant (1)
- Oil and Gas (1)
- Open Compute Project (OCP) (1)
- OpenRAN (1)
- P4 (1)
- PCIe card (1)
- PCIe lane (1)
- PCIe slot (1)
- Precision timestamping (1)
- Product life cycle (1)
- ROM (1)
- Raytheon (1)
- Remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) (1)
- Rugged computing glossary (1)
- SEDs (1)
- SIM Card (1)
- Secure boot (1)
- Sensor Open Systems Architecture (SOSA) (1)
- Small form-factor pluggable (SFP) (1)
- Smart Edge (1)
- Smart NIC (1)
- SmartNIC (1)
- Software-based CDS (1)
- Symmetric encryption (1)
- System hardening (1)
- System hardening best practices (1)
- TME (1)
- Tech Partners (1)
- Total Memory Encryption (TME) (1)
- Transfer CDS (1)
- USB ports (1)
- VMEbus International Trade Association (VITA) (1)
- Vertical Lift Consortium (VLC) (1)
- Virtual machines (1)
- What are embedded systems? (1)
- Wired access backhaul (1)
- Wireless access backhaul (1)
- accredidation (1)
- aerospace (1)
- air gaps (1)
- airborne computers (1)
- asteroid (1)
- authentication (1)
- autonomous (1)
- certification (1)
- cognitive software-defined radios (CDRS) (1)
- command and control (C2) (1)
- communications (1)
- cores (1)
- custom (1)
- customer service (1)
- customer support (1)
- data linking (1)
- data recording (1)
- ethernet (1)
- full disk encryption (1)
- hardware monitoring (1)
- heat sink (1)
- hypervisor (1)
- in-house technical support (1)
- input (1)
- integrated edge solution (1)
- international business (1)
- licensed spectrum (1)
- liquid cooling (1)
- mCOTS (1)
- microelectronics (1)
- missile defense (1)
- mixed criticality (1)
- moving (1)
- multi-factor authentication (1)
- network slicing (1)
- neural networks (1)
- new headquarters (1)
- next generation interceptor (1)
- non-volatile memory (1)
- operating system (1)
- output (1)
- outsourced technical support (1)
- post-boot (1)
- pre-boot (1)
- private networks (1)
- public networks (1)
- radio access network (RAN) (1)
- reconnaissance (1)
- rugged memory (1)
- secure flash (1)
- security (1)
- self-encrypting drives (SEDs) (1)
- sff (1)
- software (1)
- software-defined radios (SDRs) (1)
- speeds and feeds (1)
- standalone (1)
- storage (1)
- systems (1)
- tactical wide area networks (1)
- technical support (1)
- technology (1)
- third-party motherboards (1)
- troposcatter communication (1)
- unlicensed spectrum (1)
- volatile memory (1)
- vpx (1)
- zero trust network (1)
- January 2025 (1)
- November 2024 (1)
- October 2024 (1)
- August 2024 (1)
- July 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (1)
- April 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (1)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (7)
- April 2023 (5)
- March 2023 (7)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (6)
- October 2022 (7)
- September 2022 (8)
- August 2022 (3)
- July 2022 (4)
- June 2022 (13)
- May 2022 (10)
- April 2022 (4)
- March 2022 (11)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (4)
- December 2021 (1)
- November 2021 (4)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (1)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (3)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (3)
- March 2021 (3)
- February 2021 (8)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (5)
- November 2020 (5)
- October 2020 (4)
- September 2020 (4)
- August 2020 (6)
- July 2020 (9)
- June 2020 (11)
- May 2020 (13)
- April 2020 (8)
- February 2020 (1)
- January 2020 (1)
- October 2019 (1)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (2)
- March 2019 (1)
- January 2019 (2)
- December 2018 (1)
- November 2018 (2)
- October 2018 (5)
- September 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (1)
- April 2018 (2)
- March 2018 (1)
- February 2018 (9)
- January 2018 (27)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (3)
/Trenton%20Systems%20Circular%20Logo-3.png?width=50&height=50&name=Trenton%20Systems%20Circular%20Logo-3.png)
No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think